In this tutorial, we will build a Real-Time Voice Translator using Python. This project combines multiple libraries, such as Tkinter for GUI, SpeechRecognition for audio input, gTTS for text-to-speech, and GoogleTranslator for translation. The translator will allow users to speak, recognize speech, translate it into a chosen language, and listen to the translation in real-time.
Why Create a Voice Translator in Python?
A voice translator offers an excellent opportunity to combine several technologies, including voice recognition, language translation, and GUI development. This project can:
- Assist in learning new languages.
- Enable communication across linguistic barriers.
- Be a foundation for building more advanced multilingual applications.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure you have the following installed:
- Python 3.x
Tkinterfor GUIgTTS,speech_recognition,playsound,deep_translator, andthreadinglibraries
Install the necessary libraries using:
pip install gTTS speechrecognition playsound deep-translator
Code Snippet
import os
import threading
import tkinter as tk
from gtts import gTTS
from tkinter import ttk
import speech_recognition as sr
from playsound import playsound
from deep_translator import GoogleTranslator
# GUI Configuration
win = tk.Tk()
win.geometry("700x450")
win.title("Real-Time Voice🎙️ Translator🔊")
# Icon Setup
icon = tk.PhotoImage(file="icon.png")
win.iconphoto(False, icon)
# Labels and Text Boxes
input_label = tk.Label(win, text="Recognized Text ⮯")
input_label.pack()
input_text = tk.Text(win, height=5, width=50)
input_text.pack()
output_label = tk.Label(win, text="Translated Text ⮯")
output_label.pack()
output_text = tk.Text(win, height=5, width=50)
output_text.pack()
blank_space = tk.Label(win, text="")
blank_space.pack()
# Language Selection
language_codes = {
"English": "en", "Hindi": "hi", "Spanish": "es", "French": "fr",
"German": "de", "Chinese (Simplified)": "zh-CN", "Japanese": "ja",
"Russian": "ru", "Korean": "ko", "Tamil": "ta", "Telugu": "te"
}
language_names = list(language_codes.keys())
input_lang_label = tk.Label(win, text="Select Input Language:")
input_lang_label.pack()
input_lang = ttk.Combobox(win, values=["auto"] + language_names)
input_lang.set("auto")
input_lang.pack()
output_lang_label = tk.Label(win, text="Select Output Language:")
output_lang_label.pack()
output_lang = ttk.Combobox(win, values=language_names)
output_lang.set("English")
output_lang.pack()
blank_space = tk.Label(win, text="")
blank_space.pack()
keep_running = False
# Translator Logic
def update_translation():
global keep_running
if keep_running:
recognizer = sr.Recognizer()
with sr.Microphone() as source:
try:
audio = recognizer.listen(source)
speech_text = recognizer.recognize_google(audio, language=input_lang.get())
input_text.insert(tk.END, f"{speech_text}\n")
translated_text = GoogleTranslator(source=input_lang.get(), target=output_lang.get()).translate(speech_text)
output_text.insert(tk.END, translated_text + "\n")
voice = gTTS(translated_text, lang=output_lang.get())
voice.save("voice.mp3")
playsound("voice.mp3")
os.remove("voice.mp3")
except Exception as e:
output_text.insert(tk.END, f"Error: {e}\n")
win.after(100, update_translation)
def run_translator():
global keep_running
keep_running = True
threading.Thread(target=update_translation).start()
def kill_execution():
global keep_running
keep_running = False
# Buttons
run_button = tk.Button(win, text="Start Translation", command=run_translator)
run_button.place(relx=0.25, rely=0.9, anchor="c")
kill_button = tk.Button(win, text="Kill Execution", command=kill_execution)
kill_button.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.9, anchor="c")
win.mainloop()
Explanation of Key Features
1. Language Selection Dropdowns
- Enables users to select the input and output languages.
- Defaults to
autofor input andEnglishfor output.
2. Speech Recognition and Translation
- Captures audio input using the
speech_recognitionlibrary. - Translates recognized text using
deep-translator.
3. Real-Time Audio Playback
- Converts translated text to speech using
gTTS. - Plays the audio file using
playsound.
OUTPUT
The application starts with a GUI window. Users can:
- Speak into the microphone.
- View recognized text in the input box.
- See and hear the translation in real-time.
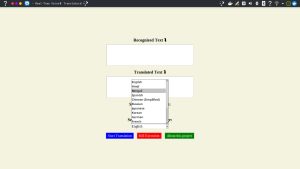
OUTPUT 1 : Speech-to-Speech-Translation
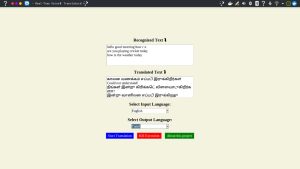
OUTPUT 2 : Speech-to-Speech-Translation
Code Explanation: Real-Time Voice Translator
Here’s a detailed explanation of the code for your real-time voice translator application, broken down section by section:
1. Importing Libraries
import os import threading import tkinter as tk from gtts import gTTS from tkinter import ttk import speech_recognition as sr from playsound import playsound from deep_translator import GoogleTranslator
os: To handle file operations like saving and deleting audio files.threading: For running processes (e.g., speech recognition) without freezing the GUI.tkinter: To create the graphical user interface.gTTS: To convert translated text into speech.speech_recognition: For real-time speech recognition from the microphone.playsound: To play the generated speech audio.deep_translator.GoogleTranslator: For translating recognized speech into another language.
2. Tkinter Window Setup
win = tk.Tk()
win.geometry("700x450")
win.title("Real-Time Voice🎙️ Translator🔊")
icon = tk.PhotoImage(file="icon.png")
win.iconphoto(False, icon)
win = tk.Tk(): Creates the main window for the application.geometry: Sets the size of the window.title: Sets the title of the application.iconphoto: Adds a custom icon for the application window.
3. Creating Input and Output Text Fields
input_label = tk.Label(win, text="Recognized Text ⮯") input_label.pack() input_text = tk.Text(win, height=5, width=50) input_text.pack() output_label = tk.Label(win, text="Translated Text ⮯") output_label.pack() output_text = tk.Text(win, height=5, width=50) output_text.pack()
Label: Displays static text (titles for input and output fields).Text: Creates text boxes for displaying recognized and translated text.pack(): Places the elements in the window.
4. Language Dropdown Menus
language_codes = {...} # Dictionary of languages and their codes
language_names = list(language_codes.keys())
input_lang_label = tk.Label(win, text="Select Input Language:")
input_lang_label.pack()
input_lang = ttk.Combobox(win, values=language_names)
input_lang.bind("<<ComboboxSelected>>", lambda e: update_input_lang_code(e))
input_lang.pack()
language_codes: Maps language names to their respective codes (used for translation).Combobox: A dropdown menu for selecting languages.bind(): Updates the selected language code when a language is chosen.
Similar setup applies to the output language dropdown menu.
5. Translation Logic
Global Variable and Main Function
keep_running = False
def update_translation():
global keep_running
...
win.after(100, update_translation)
keep_running: Tracks whether the application is actively listening and translating.update_translation(): Continuously listens for speech, translates it, and plays the audio ifkeep_runningisTrue.
Speech Recognition
r = sr.Recognizer()
with sr.Microphone() as source:
audio = r.listen(source)
speech_text = r.recognize_google(audio)
sr.Recognizer: Initializes the recognizer object.sr.Microphone(): Accesses the default microphone.r.listen(): Captures audio input.r.recognize_google(): Converts the audio input to text using Google’s speech recognition API.
Translation and Text-to-Speech
translated_text = GoogleTranslator(source=input_lang.get(), target=output_lang.get()).translate(text=speech_text)
voice = gTTS(translated_text, lang=output_lang.get())
voice.save('voice.mp3')
playsound('voice.mp3')
os.remove('voice.mp3')
GoogleTranslator: Translates the recognized text into the selected output language.gTTS: Converts translated text into speech.playsound: Plays the generated audio.os.remove: Deletes the audio file after playing it.
6. Starting and Stopping Translation
def run_translator():
global keep_running
if not keep_running:
keep_running = True
threading.Thread(target=update_translation).start()
def kill_execution():
global keep_running
keep_running = False
run_translator(): Starts the translation process by settingkeep_runningtoTrueand runningupdate_translation()in a separate thread.kill_execution(): Stops the translation process by settingkeep_runningtoFalse.
7. Buttons for User Control
run_button = tk.Button(win, text="Start Translation", command=run_translator) run_button.place(relx=0.25, rely=0.9, anchor="c") kill_button = tk.Button(win, text="Kill Execution", command=kill_execution) kill_button.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.9, anchor="c")
Button: Creates buttons for starting and stopping the translation process.place(): Positions the buttons in the window.
8. Event Loop
win.mainloop()
Keeps the application running, listening for user inputs and interactions.
Improvements and Suggestions
- Error Handling: Already included for unknown speech and Google API errors, but consider displaying pop-ups for better user feedback.
- Thread Safety: Add locks for shared resources like
keep_runningto avoid concurrency issues. - UI Enhancement: Add additional UI features like a progress bar or status indicator.
LINKS :
Direct Speech-to-Speech Translation
Speech-to-Speech translation using Deep Learning