Form Validation is a crucial part of web development. It ensures that users enter accurate and complete information before submitting a form. JavaScript commonly gives immediate feedback for client-side validation without requiring a page reload. This blog will explore the basics of JavaScript form validation, including essential techniques and a sample code.
why Form Validation Matters
Form validation is essential for Data Integrity to ensure the data submitted by users is accurate and complete, for User Experience to provide immediate feedback, and for Security to prevent malicious input.
Techniques for JavaScript Form Validation
- Require Fields: Make sure to fill out all required fields.
- Data Type Validation: Ensure the input matches the expected data type; for example, email or number.
- Length Validation: Verify the input length of the limit.
Example of Form Validation Using JavaScript
Let’s look at an example of a simple form validation script using JavaScript. The below example validates the name and password to meet specific criteria.
<!--validating the name and password--> <html> <title>Form Validation using JavaScript</title> <head> </head> <body> <script src = fm.js></script> <body> <form name = "myform" method = "post" onsubmit = "return ValidateForm()" > Name: <input type = "text" name = "name"><br/> Password: <input type = "password" name = "password"><br/> <input type = "submit" value = "register"> </form> </body> </html>
The above HTML code creates a simple form with fields for name and password. It includes a script(‘fm. js’ file) for form validation. When the user submits the form, the ‘ ValidateForm( ) ‘ function from ‘fm.js’ runs. Consequently, the system prevents the form submission if ‘ ValidateForm( ) ‘ returns false.
function ValidateForm(){
var name = document.myform.name.value;
var password = document.myform.password.value;
if (name == null || name == ""){
alert("Name must be filled it can't be blank");
return false;
}
else if(password.length < 5){
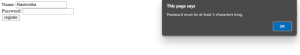
alert("Password must be at least 5 characters long.");
return false;
}
}
The above JavaScript function checks if the name field is empty and it verifies if the password is less than 5 characters. It alerts the user if validation fails and prevents form submission.
Output:
The below outputs display the pop-up box if we didn't Validate the form.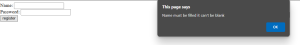
After entering the correct user details, the user successfully submits the form, and the server saves the data.
Visit the link for email Validation: Email ID validation using JavaScript.
Conclusion
JavaScript is a web-based essential tool for client-side form validation, it provides immediate feedback and, therefore, improves the overall user experience. By implementing the techniques shown above, you can ensure the data collected through forms is accurate and complete, reducing the likelihood of errors and enhancing the security of your web application.