Table of Content
- What is JSON?
- Advantages of using JSON format
- Methods
- How JSON Increases Code Readability
- Examples in Real-time React application
In this Blog, We will learn how JSON data format is used in JavaScript and makes life much easier. As we know JavaScript is a popular
language and is responsible for the functionality of the website like navigation, animation, and more.
JSON in JavaScript
What is JSON?
JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation. It is a way to represent Data in the form of Objects. Objects are a collection of properties with key and value pairs. It is defined within “{ }” curly brackets.
Example of JSON data:
const data = {
"name": "Gary",
"Roll-no": 24,
"hobbies":['Football','Badminton','Coding']
}
Advantages of Using JSON format
These are the Following Reasons to use JSON in JavaScript:
- Readability: It increases the readability of the code as all the data is stored in a single file and can be imported onto different coding files in JavaScript.
- Agility: JSON data is used on both the front-end and back-end. i.e. The fetched Data from an API in JSON is easily integrated with the front end of a web app.
- Dynamic: can be easily changed in different data formats (like YAML data format).
Methods
1. JSON.Parse():
It is a static method that converts the JSON data to a format the back-end server can understand.
Example:
const users = {
"Name":"Srisanth",
"isVerified": true,
"Media":[ "Image1", "Image2" ],
"Login": "2024-01-05,10:30:00"
}
const data = JSON.parse(users);
2. JSON.stringify():
The stringify() method helps in fetching data from an API endpoint and returns it in a JSON string.
Example :
let apiUrl = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users"
const fetchData = async () =>{
try{
const Data = await fetch(apiUrl,{
method: 'GET',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify()
})
const response = await Data.json()
console.log("Response", response)
}
catch(error){
console.log("Error", error)
}
}
Here, the “fetch data” function makes a GET request using the fetch function to the API URL endpoint and returns the data in JSON format.
How does JSON increase readability?
Let’s understand with the help of an example. Let’s say you want you are building an E-commerce platform and want to list the items on the site. A solution for this can be adding the items manually. But it hampers code readability and adding thousands of items is not possible. Here comes the JSON in action. The most appropriate solution is to use JSON. We list all the items with their properties and use the map function to iterate over the list of JSON objects and display them on the site.
Example:
Using React framework to showcase the functionality of JSON in javascript
Let’s say this is the data you want to display the below data.
NOTE: you can refer to this resource for a better understanding :
Setting up a React app
First, store it in a file called data.js in the src folder.
const Data ={
"Watches":[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Rolex",
"price": 100,
"description": "Luxury Watch",
"status": "Available"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Titan",
"price": 50,
"description": "Casual Watch",
"status": "Available"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Fastrack",
"price": 20,
"description": "Sports Watch",
"status": "Available"
}
],
"Shirts":[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Peter England",
"price": 100,
"description": "Formal Shirt",
"status": "Available"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Raymond",
"price": 50,
"description": "Casual Shirt",
"status": "Available"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Levis",
"price": 20,
"description": "Denim Shirt",
"status": "Available"
}
],
"Shoes":[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Nike",
"price": 100,
"description": "Sports Shoes",
"status": "Available"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Reebok",
"price": 50,
"description": "Casual Shoes",
"status": "Available"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Adidas",
"price": 20,
"description": "Formal Shoes",
"status": "Available"
}
]
}
export default Data;
Now, we can import the Data.js file to the App.js. and use the map function to iterate the Data and display it on the E-commerce Website.
import React from 'react'
import Data from './Data'
import './App.css'
const App = () => {
return (
<div className='card'>
{Data?.Watches?.map((watch) => (
<div className='content'key={watch.id}>
<h1>{watch.name}</h1>
<p>{watch.price}</p>
<p>{watch.description}</p>
<p>{watch.status}</p>
</div>
))}
{Data?.Shirts?.map((shirt) => (
<div className='content' key={shirt.id}>
<h1>{shirt.name}</h1>
<p>{shirt.price}</p>
<p>{shirt.description}</p>
<p>{shirt.status}</p>
</div>
))}
{Data?.Shoes?.map((shoe) => (
<div className='content' key={shoe.id}>
<h1>{shoe.name}</h1>
<p>{shoe.price}</p>
<p>{shoe.description}</p>
<p>{shoe.status}</p>
</div>
))}
</div>
)
}
export default App
Here is the Final Output, As we can see the App.js is much more readable than adding data manually.
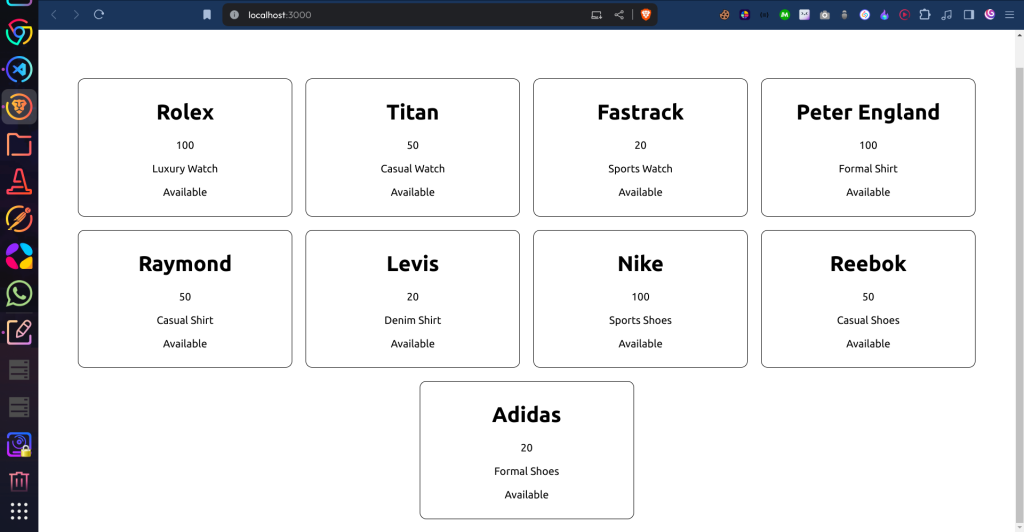
In Conclusion, We can say that JSON improves the performance of the website because of its lightweight behavior, improves the readability of the code, and aids the connectivity of Frontend to the Backend code (i.e. Server) as data is easily transmitted between the servers.