The window object in JavaScript is a global object representing the browser’s window. It’s the root object of the Document Object Model (DOM) and contains methods, properties, and events that are essential for web development. Whether interacting with the document, handling events, or managing storage, the ‘window’ object is the gateway to it all.
In this tutorial, let’s explore some key aspects of the window object with simple examples and their outputs.
What is ‘Window’ object?
The window object is the top-level object in the browser’s JavaScript hierarchy. It acts as a global container for various functionalities, such as displaying alerts, manipulating documents, and handling user interactions.
Basic properties of Window object:
- window.document: Represents the HTML document loaded in the window. It’s a gateway to interact with the DOM (Document Object Model).
- window.location: Provides information about the current URL and allows you to navigate to different URLs.
- window.history: Provides methods to interact with the browser’s session history (i.e., the pages visited in the tab or frame).
- window.navigator: Contains information about the browser and the operating system.
- window.screen: Provides information about the user’s screen.
Basic methods of window object:
- window.alert(): Displays an alert box with a message.
- window.confirm(): Displays a dialog box with a message and “OK” and “Cancel” buttons.
- window.prompt(): Displays a dialog box that prompts the user for input.
- window.open(): Opens a new browser window or tab.
- window.close(): Closes the current window.
Example of window object in JavaScript
Let’s look at an example of a window object in JavaScript using some Properties and Methods.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Window Object Example</title>
<script src=window.js>
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Window Object Example</h1>
<button onclick="showAlert()">Show Alert</button>
<button onclick="showConfirm()">Show Confirm</button>
<button onclick="showPrompt()">Show Prompt</button>
<button onclick="navigate()">Go to Example.com</button>
</body>
</html>
This HTML document demonstrates the use of the window object with four buttons triggering JavaScript functions (showAlert, showConfirm, showPrompt, navigate). The script window.js contains these functions, which interact with the user via alerts, prompts, and navigation.
Output: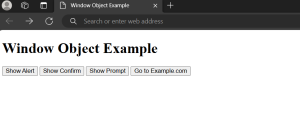
<!--This is window.js file-->
function showAlert() {
window.alert("This is an alert message!");
}
function showConfirm() {
var result = window.confirm("Do you want to proceed?");
if (result) {
window.alert("You chose OK.");
} else {
window.alert("You chose Cancel.");
}
}
function showPrompt() {
var userInput = window.prompt("Please enter your name:", " ");
if (userInput !== null) {
window.alert("Hello, " + userInput + "!");
}
}
function navigate() {
window.location.href = "https://www.codespeedy.com";
}
This JavaScript code defines four functions to show alert, confirmation, and prompt dialogs, and to navigate to “https://www.codespeedy.com” using the window object methods.
Output: By clicking on Show Alert, the below output is displayed.By clicking on show confirm, the below output is displayed.
By clicking on the show prompt, the below output is displayed.
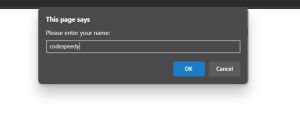
By clicking on the Go to Example.com it will navigate to the related webpage.
Conclusion:
The window object is an essential part of web development in JavaScript. It provides numerous properties and methods to interact with the browser and enhance the user experience. This simple example demonstrates basic interactions using the ‘window’ object. With the properties and methods of the window object, you can create dynamic, responsive, and interactive web applications that enhance user experience.