While designing graphical applications in Python using Tkinter, sometimes you may want to be able to dynamically alter the size of the window according to user actions or any other conditions. Tkinter offers several ways of changing window properties, including size. In this blog we will be changing Tkinter window size through variables.
Method 1: Through variables in our code.
Step 1 : Basic Tkinter window
First, we will create a Tkinter window of the default view 400×300 pixels. This window is resizable, and the user can easily change its size by dragging its edges.
import tkinter as tk
# Create the main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Resizable Window Example")
# Set the initial window size
root.geometry("400x300")
# Run the application
root.mainloop()
Output:

Step 2 : Taking User Input variables to change the window size
Now, let us implement window size by variables. For this purpose, declare two variables: one for width and another for height. These variables change the size of the window as per our requirement.
import tkinter as tk
# Create the main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Resizable Window Example")
# Initialize variables for width and height
width_var = 400
height_var = 300
#Applying changes through variables in the code
root.geometry(f"{width_var}x{height_var}")
# Run the application
root.mainloop()
In this code, when we manually change the values of width_var and height_var in the code, we can run the program to get new window size.
Output:
On running this code, we get default window with current size i.e. 400×300 pixels.

Now in our code, we change the value of the variables like this:
# Initialize variables for width and height width_var = 500 height_var = 600
Then we get the following output:

This method is better explained in the following video.
Method 2: Through user input variables.
Step 1 : Basic Tkinter window
First, we will create a Tkinter window of the default view 400×300 pixels. This window is resizable, and the user can easily change its size by dragging its edges.
import tkinter as tk
# Create the main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Resizable Window Example")
# Set the initial window size
root.geometry("400x300")
# Run the application
root.mainloop()
Output:

Step 2 : Taking User Input variables to change the window size
Now, let us implement window size by variables. For this purpose, declare two variables: one for width and another for height. These variables change the size of the window as per our requirement.
import tkinter as tk
def update_size():
width = width_var.get()
height = height_var.get()
root.geometry(f"{width}x{height}")
# Create the main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Resizable Window Example")
# Initialize variables for width and height
width_var = tk.IntVar(value=400)
height_var = tk.IntVar(value=300)
# Set the initial window size
root.geometry(f"{width_var.get()}x{height_var.get()}")
# Create entry widgets to change window size
width_entry = tk.Entry(root, textvariable=width_var)
width_entry.pack(pady=10)
height_entry = tk.Entry(root, textvariable=height_var)
height_entry.pack(pady=10)
# Create a button to apply the size changes
apply_button = tk.Button(root, text="Apply Size", command=update_size)
apply_button.pack(pady=10)
# Run the application
root.mainloop()
In the example above we will initialize width_var and height_var as Tkinter IntVar variables. These variables contain the window’s width and height respectively. We setup their values initially for 400 and 300. The update_size function fetches these values and applies the window size using the geometry method.
Output:
On running this code, we get default window with current size i.e. 400×300 pixels.
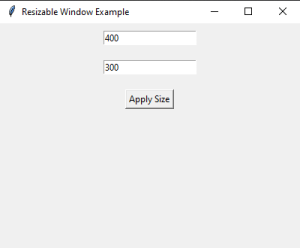
In this, we enter the height and width of the window we desire. for example, let us take the desired height and width to be 800*200 pixels. We will enter the size in the given input field and press the Apply Size button.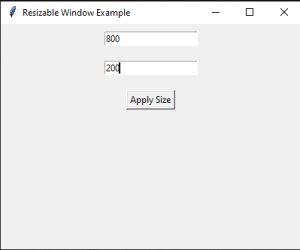
After pressing the Apply Size button, we can see that the window has resized to the desired size.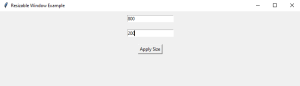
Conclusion:
Variables-controlled Tkinter window size can provide a very flexible way for creating dynamic and responsive GUIs inside a window. The variables for width and height are defined, Entry widgets are used to acquire the user’s input, and then change the size of the window according to the condition. You can try running the examples above to add such functionality to your Tkinter apps.