What is Blurring and Smoothing?
Blurring or smoothing is a fundamental image processing technique that involves reducing the detail and noise in an image. It works by averaging or filtering the pixel value in a neighborhood around each pixel to produce a softer, less detailed picture. In Python, especially using libraries like OpenCV, blurring is applied using various convolution techniques or filters that process the pixel values based on their surrounding pixels.
Blurring and smoothing images are standard preprocessing techniques in image processing to reduce noise and detail. For using this, we can use the Python libraries like OpenCV.

Definition
“Blurring or Smoothing is the process of reducing image noise and sharpness by modifying the pixel intensity values through averaging or statistical operations over a defined neighborhood (kernel), resulting in a less detailed version of the original image.”
Health Challenge Tracker
OpenCV Documentation
What is a Gaussian Filter?
A Gaussian filter is a filter that can be used in image processing, which uses a Gaussian Kernel to smooth images, preserving edges better than a simple average. Using this filter in Python, we can use the OpenCV libraries.
It can smooth the image by averaging nearby pixels, where pixels closer to the center of the kernel have more weight.
When to use it:
- When you want to achieve a neutral blurring effect.
- When dealing with Gaussian noise.
- For smoothing before edge detection.

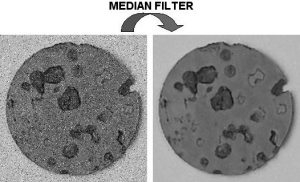
What is a Median Filter?
A median filter processes an image by replacing each pixel with the median value of its neighborhood, making it excellent for removing “salt and pepper” noise.
When to use it:
- When the image has an outlier.
- For noise reduction without losing edges.
For OpenCV library first install in python editor in your system by following command:
pip install opencv-python
Example:
import cv2 # OpenCV library for image processing
import numpy as np # NumPy for numerical operations
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Matplotlib for plotting images
# Put the image
img = cv2.imread('image.jpg.png')
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.color_BGR2RGB)
# Gaussian Blur
gaussian_blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(ing_rgb, (5, 5), 0)
# Midian Blur
median_blure = cv2.medianBlur(img_rgb, 5)
# Result
plt.figure(figsize = (12, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
plt.title('Original Image')
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(gaussian_blur)
plt.title('Gaussian Filter')
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(median_blur)
plt.title('Midian Filter')
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output:

Original code link: OpenCV code
Python Tools for Blurring:
- OpenCV: Most widely used for image processing.
- SciPy: Offers filtering functions.
- PIL/Pillow: For basic blur operations.
- NumPy: For manual implementation of filters.
Convert an image into grayscale in Python OpenCV
Detecting and Preventing Code Injection Attacks in Python
Tutorial on uploading Files with Flask | Python