As per my knowledge,
Python has a standard GUI (Graphical user interface) that is Tkinter. It has the widgets tool. Here the main role of widgets is to provide a good variety of control. Labels are an example of widgets. Changing a Windows label text dynamically is very easy by following a few steps-
- At first create a Tkinter application basically import the modules of Tkinter.
- Then create the main window.
- After that create a label into the lt function.
- Then create a variable and use the Tkinter in-build function.
- Then use the set method, it is basically whatever value I am putting here that will be stored in the variable.
- Then use the label function for creating the label widget and it’s important that we use the text variable.
- After that creating a button use Tkinter’s own button function in this add some text and the command will be the function name for attaching with the counter function.
- In this way we can change a label text.
Note that pack() is place the label in the Tkinter window. Tkinter have this pack geometry which is organize the widgets. Tkinter support 3 geometry managers
pack
grid
place
The pack manager has many features to manage to widgets-
Side
Expand
Anchor
import tkinter as haswati
newWindow=haswati.Tk()
newWindow.geometry("300x300+100+50")
def lt():
variable=haswati.StringVar()
variable.set("Thank you for pressing me")
label=haswati.Label(newWindow,textvariable=variable)
label.pack()
click=haswati.Button(newWindow, text="Press", command=lt)
click.pack()
newWindow.mainloop()
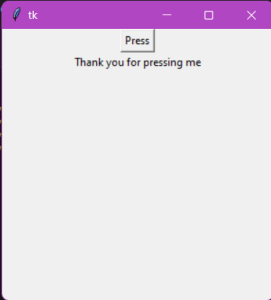
Output:
when the code we run we have to a button which is
Press.

After that when we click it then it shown like-