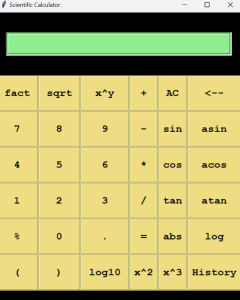
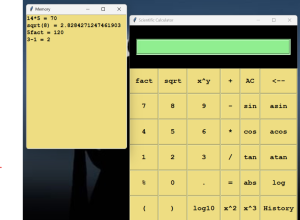
Introduction
In this program , we will create a scientific calculator using tkinter library in python , which provides a graphical user interface (gui) for inputting and calculating mathematical expressions.
This scientific calculator performs basic arithmetic operations, advanced mathematical functions (fact,abs,log,sqrt), trigonometry functions and power functions
This scientific calculator has a history feature which Records and displays a history of all calculations performed, allowing users to review previous calculations
Program
Here is the full program to create a scientific calculator using tkinter
import tkinter as tk
from math import sin, cos, tan, log, sqrt, pi, exp, asin, acos, atan, fabs, factorial, radians, log10
history = []
def input_click(value):
current_text = input_field.get()
input_field.delete(0, tk.END)
input_field.insert(tk.END, current_text + value)
def trigonometry(func, value):
try:
if func in ['sin', 'cos', 'tan', 'asin', 'acos', 'atan']:
value = radians(value) if value <= 180 else value
if func == 'sin':
return sin(value)
elif func == 'cos':
return cos(value)
elif func == 'tan':
return tan(value)
elif func == 'asin':
return asin(value)
elif func == 'acos':
return acos(value)
elif func == 'atan':
return atan(value)
except Exception as e:
return "Error"
def calculate():
try:
expression = input_field.get()
if "fact" in expression:
num = int(expression.replace("fact", "").strip())
result = factorial(num)
elif "abs" in expression:
num = float(expression.replace("abs", "").strip())
result = fabs(num)
elif "log10" in expression:
num = float(expression.replace("log10", "").strip())
result = log10(num)
elif "log" in expression:
num = float(expression.replace("log", "").strip())
result = log(num)
elif "x^2" in expression:
num = float(expression.replace("x^2", "").strip())
result = num ** 2
elif "x^3" in expression:
num = float(expression.replace("x^3", "").strip())
result = num ** 3
else:
for trig_func in ['sin', 'cos', 'tan', 'asin', 'acos', 'atan']:
if trig_func in expression:
parts = expression.split(trig_func)
if len(parts) > 1:
value = float(parts[1].strip('()'))
result = trigonometry(trig_func, value)
input_field.delete(0, tk.END)
input_field.insert(tk.END, f"{result:.8f}")
history.append(f"{expression} = {result:.8f}")
return
expression = expression.replace('x^y', '**')
result = eval(expression)
input_field.delete(0, tk.END)
input_field.insert(tk.END, (result))
history.append(f"{expression} = {result}")
except Exception as e:
input_field.delete(0, tk.END)
input_field.insert(tk.END, "Error")
def all_clear():
input_field.delete(0, tk.END)
def backspace():
current_text = input_field.get()
input_field.delete(0, tk.END)
input_field.insert(tk.END, current_text[:-1])
def show_memory():
memory_window = tk.Toplevel(calculator_window)
memory_window.geometry("300x400")
memory_window.title("Memory")
memory_listbox = tk.Listbox(memory_window, font="courier 13 bold", bg="lightgoldenrod")
memory_listbox.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
for entry in history:
memory_listbox.insert(tk.END, entry)
calculator_window = tk.Tk()
calculator_window.geometry("500x600")
calculator_window.title("Scientific Calculator")
calculator_window.configure(bg="black")
input_field = tk.Entry(calculator_window, font="courier 24", bd=5, bg="lightgreen", relief="groove", justify="right")
input_field.grid(row=2, column=0, columnspan=6, sticky="nsew", pady=40, padx=20)
row = 3
col = 0
calc_buttons = [
"fact", "sqrt", "x^y", "+", "AC", "<--",
"7", "8", "9", "-", "sin", "asin",
"4", "5", "6", "*", "cos", "acos",
"1", "2", "3", "/", "tan", "atan",
"%", "0", ".", "=", "abs", "log",
"(", ")", "log10", "x^2", "x^3", "History"
]
for button in calc_buttons:
if button == "=":
num_btn = tk.Button(calculator_window, text=button, font="courier 16 bold", command=calculate, relief="groove", bg="lightgoldenrod")
elif button == "AC":
num_btn = tk.Button(calculator_window, text=button, font="courier 16 bold", command=all_clear, relief="groove", bg="lightgoldenrod")
elif button == "<--":
num_btn = tk.Button(calculator_window, text=button, font="courier 16 bold", command=backspace, relief="groove", bg="lightgoldenrod")
elif button == "History":
num_btn = tk.Button(calculator_window, text=button, font="courier 16 bold", command=show_memory,relief="groove",bg="lightgoldenrod")
else:
num_btn = tk.Button(calculator_window, text=button, font="courier 16 bold", command=lambda value=button: input_click(value), relief="groove", bg="lightgoldenrod")
num_btn.grid(row=row, column=col, sticky="nsew")
col += 1
if col > 5:
col = 0
row += 1
for i in range(3):
calculator_window.grid_columnconfigure(i, weight=1)
for i in range(3, row + 1):
calculator_window.grid_rowconfigure(i, weight=1)
calculator_window.mainloop()
Program Explanation
Lets us breakdown the program into smaller parts to understand easily:
Importing Necessary Libraries
import tkinter as tk from math import sin, cos, tan, log, sqrt, pi, exp, asin, acos, atan, fabs, factorial, radians, log10
The tkinter library is imported, which is used to create a graphical user interface.
The math library provides functions such as trigonometric (sin , cos etc.), logarithmic (log, log10), and other mathematical operations (square root, factorial etc.) used in the calculator.
Global variable
history = []
this list is created to store the calculations performed by the calculator
Input Handling function
def input_click(value):
current_text = input_field.get()
input_field.delete(0, tk.END)
input_field.insert(tk.END, current_text + value)
This function updates the input field by appending the value of the clicked button to the current text in the field.
Trigonometric calculations function
def trigonometry(func, value):
try:
if func in ['sin', 'cos', 'tan', 'asin', 'acos', 'atan']:
value = radians(value) if value <= 180 else value
if func == 'sin':
return sin(value)
elif func == 'cos':
return cos(value)
elif func == 'tan':
return tan(value)
elif func == 'asin':
return asin(value)
elif func == 'acos':
return acos(value)
elif func == 'atan':
return atan(value)
except Exception as e:
return "Error"
This function handles trigonometric calculations like sine, cosine, and tangent. It also converts angles to radians if they are less than or equal to 180 degrees.
Main Calculation logic
def calculate():
try:
expression = input_field.get()
if "fact" in expression:
num = int(expression.replace("fact", "").strip())
result = factorial(num)
elif "abs" in expression:
num = float(expression.replace("abs", "").strip())
result = fabs(num)
elif "log10" in expression:
num = float(expression.replace("log10", "").strip())
result = log10(num)
elif "log" in expression:
num = float(expression.replace("log", "").strip())
result = log(num)
elif "x^2" in expression:
num = float(expression.replace("x^2", "").strip())
result = num ** 2
elif "x^3" in expression:
num = float(expression.replace("x^3", "").strip())
result = num ** 3
the expression typed in the input field is stored in the expression variable.
The if condition checks for specific keywords like fact, abs, log, log10, x^2, and x^3 to perform corresponding operations such as calculating factorials, absolute values, logarithms, and exponentiation. Each operation retrieves the necessary number from the input, performs the calculation, and stores the result.
Handling trigonometric functions
else:
for trig_func in ['sin', 'cos', 'tan', 'asin', 'acos', 'atan']:
if trig_func in expression:
parts = expression.split(trig_func)
if len(parts) > 1:
value = float(parts[1].strip('()'))
result = trigonometry(trig_func, value)
input_field.delete(0, tk.END)
input_field.insert(tk.END, f"{result:.8f}")
history.append(f"{expression} = {result:.8f}")
return
This block of code handles trigonometric functions and uses the trigonometry function to calculate the result
Handling general expressions
expression = expression.replace('x^y', '**')
result = eval(expression)
This part handles general mathematical expressions (like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division)
Updating the input field
input_field.delete(0, tk.END)
input_field.insert(tk.END, (result))
history.append(f"{expression} = {result}")
except Exception as e:
input_field.delete(0, tk.END)
input_field.insert(tk.END, "Error")
The result is inserted into the input field, and if an error occurs, an “Error” message is displayed.
Function to clear the input field
def all_clear():
input_field.delete(0, tk.END)
this function clears the input field
Backspace function
def backspace():
current_text = input_field.get()
input_field.delete(0, tk.END)
input_field.insert(tk.END, current_text[:-1])
This function allows the user to delete the last entered character
Displaying Calculation History
def show_memory():
memory_window = tk.Toplevel(calculator_window)
memory_window.geometry("300x400")
memory_window.title("Memory")
memory_listbox = tk.Listbox(memory_window, font="courier 13 bold", bg="lightgoldenrod")
memory_listbox.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
for entry in history:
memory_listbox.insert(tk.END, entry)
This function creates a new window displaying all the previous calculations stored in history
Setting Up the Tkinter Window
calculator_window = tk.Tk()
calculator_window.geometry("500x600")
calculator_window.title("Scientific Calculator")
calculator_window.configure(bg="black")
This block initializes the main calculator window and configures its appearance.
Creating the Input Field
input_field = tk.Entry(calculator_window, font="courier 24", bd=5, bg="lightgreen", relief="groove", justify="right") input_field.grid(row=2, column=0, columnspan=6, sticky="nsew", pady=40, padx=20)
This creates an input field where the user can enter numbers and expressions. It spans 6 columns and is centered
Defining Calculator Buttons
calc_buttons = [
"fact", "sqrt", "x^y", "+", "AC", "<--",
"7", "8", "9", "-", "sin", "asin",
"4", "5", "6", "*", "cos", "acos",
"1", "2", "3", "/", "tan", "atan",
"%", "0", ".", "=", "abs", "log",
"(", ")", "log10", "x^2", "x^3", "History"
]
This list defines all the buttons that will be displayed on the calculator.
Creating Button Widgets
for button in calc_buttons:
if button == "=":
num_btn = tk.Button(calculator_window, text=button, font="courier 16 bold", command=calculate, relief="groove", bg="lightgoldenrod")
elif button == "AC":
num_btn = tk.Button(calculator_window, text=button, font="courier 16 bold", command=all_clear, relief="groove", bg="lightgoldenrod")
elif button == "<--":
num_btn = tk.Button(calculator_window, text=button, font="courier 16 bold", command=backspace, relief="groove", bg="lightgoldenrod")
elif button == "History":
num_btn = tk.Button(calculator_window, text=button, font="courier 16 bold", command=show_memory,relief="groove",bg="lightgoldenrod")
else:
num_btn = tk.Button(calculator_window, text=button, font="courier 16 bold", command=lambda value=button: input_click(value), relief="groove", bg="lightgoldenrod")
This loop iterates over each button in calc_button and creates a button widget for each. It sets the appropriate command for each button.
Placing Buttons in grid layout
num_btn.grid(row=row, column=col, sticky="nsew")
col += 1
if col > 5:
col = 0
row += 1
This code places the buttons in a grid layout. When a row is filled (6 buttons per row), it moves to the next row.
Configuring Grid Weight
for i in range(3):
calculator_window.grid_columnconfigure(i, weight=1)
for i in range(3, row + 1):
calculator_window.grid_rowconfigure(i, weight=1)
This section configures the layout to allow the rows and columns to expand and contract dynamically.
Main loop
calculator_window.mainloop()
This starts the main loop of the Tkinter window, keeping the application running and responsive to user input.
Output