This article introduces the Python subprocess module, which is used to run external commands and interact with system processes. It explains basic functions like subprocess.run(), which executes commands, captures output, and handles errors. The article also demonstrates creating a custom Bash script, setting execute permissions, and running it through Python, showing how Python automates system-level tasks.
Subprocess:
The subprocess in Python has a module that provides a way to run and manage external processes from within a Python script. This allows you to spread new procedures, interact with them, and get their results (such as their output, error messages and return codes).
Basic Functions In subprocess Module:
subprocess.run():
This is the most used function in subprocess. It runs a command and waits for it to finish.
syntax:
subprocess.run(args, *, input = None, stdin = None, stdout = None, stderr = None, input = None, capture_output = False, check = False, shell = False, text = False)
subprocess.Popen():
It is a lower-level function that provides more control over process creation and interaction.
syntax:
subprocess.Popen(args, bufsize=-1, executable=None, stdin = None, stdout = None, stderr = None, close_fds=True, shell=False, universal_newlines=False, creationflags=0)
subprocess.call():
This function is used to run a command and wait for it to complete.
It is similar to subprocess.run() but with fewer options.
It returns the exit code of the command.
syntax:
subprocess.call(args, *, stdin = None, stdout = None, stderr = None, shell = False, timeout = None)
Examples for Creating Custom Bash Scripts in Python with subprocess
Example 1: Running a Simple Bash Command.
The below python code uses subprocess.run() to execute a Bash command (echo) that prints a message. It captures the output and prints it using result.stdout in text format.
import subprocess
# Define a simple Bash command (e.g., 'echo' command)
command = "echo 'Hello, programmer this is a custom Bash script executed from Python!'"
# Execute the command
result = subprocess.run(command, shell = True, capture_output = True, text = True)
print("Output from the Bash Command")
# Output the result
print(result.stdout)
output:
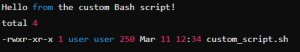
Example 2: Creating and Running a Custom Bash Script Using Python.
The below code creates a Bash script that prints a message and lists directory contents, makes it executable, and runs it using subprocess, then prints the script’s output
import subprocess
import os
# Define the content of the Bash script
bash_script_content = """#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello from the custom Bash script!"
ls -l
"""
# Write the Bash script to a file
script_path = "/tmp/custom_script.sh"
with open(script_path, 'w') as file:
file.write(bash_script_content)
# Make the script executable
os.chmod(script_path, 0o755) # Set execute permissions
# Run the script using subprocess
result = subprocess.run([script_path], capture_output=True, text=True)
# Print the output of the script
print(result.stdout)
Reference links for subprocess:
subprocess management – Python 3.7 Documentation
subprocesses — Python 3.13.2 documentation