This guide will show you how to implement AES encryption and decryption in Java from scratch. First, we introduce AES, explaining its functionality, different modes of operation, and why it is one of the most secure encryption algorithms available. Next, we provide a step-by-step tutorial, ensuring even beginners can easily understand and implement AES encryption in Java. By the end, you will know how to use encryption to secure passwords, financial transactions, and sensitive messages.
Introduction to AES
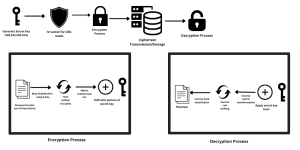
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a widely used symmetric encryption algorithm that ensures strong data security. Unlike asymmetric encryption, AES relies on a single key for both encryption and decryption, making it fast and efficient.
AES encrypts data in 16-byte blocks and supports key sizes of 128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit, allowing developers to select the desired security level.
Because of its strong encryption and high speed, AES has become the global standard for protecting sensitive data.
Modes of Operation
AES supports multiple modes of operation, each with different advantages:
1. Electronic Codebook (ECB) Mode
- Encrypts each block separately.
- Vulnerable to patterns in plaintext, making it less secure.
2. Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) Mode
- Uses an Initialization Vector (IV) so that each ciphertext block depends on the previous one.
- Prevents repeating patterns, significantly improving security.
3. Counter (CTR) Mode
- Converts AES into a stream cipher.
- Allows parallel encryption, making it highly efficient.
4. Galois/Counter Mode (GCM)
- Enhances CTR mode by adding authentication, preventing data tampering.
- Ideal for secure network communications.
For this tutorial, we use CBC mode, as it provides strong security by introducing randomness.
Generation of AES Key
AES encryption requires a secure key for both encryption and decryption. The key size determines the level of security.
package AES;
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public class AESKeyProvider {
public static SecretKey generateKey() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
KeyGenerator generator = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");
generator.init(256);
return generator.generateKey();
}
}
Explanation:
- Create an instance of a key generator which is specifically designed for the AES algorithm.
- Initialize the size of key (256 for strong encryption).
- Return the generated Key.
Generate an Initialization Vector(IV)
AES in CBC mode requires an IV (Initialization Vector) to ensure unique encryption for identical inputs.
package AES;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
public class AESIVProvider {
public static IvParameterSpec generateIv(){
byte[] iv = new byte[16];
new SecureRandom().nextBytes(iv);
return new IvParameterSpec(iv);
}
}
Explanation:
- Define a 16-byte array as AES works on 16-byte blocks.
- Using SecureRandom to fill the array with random bytes, ensuring uniqueness for same input.
- Wrap the obtained iv array in IvParameterSpec class, which will be required for encryption and decryption.
Encryption Using AES
The AESEncryption class encrypts plaintext using AES in CBC mode with PKCS5 padding.
package AES;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import java.util.Base64;
public class AESEncryption {
private static final String ALGO = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
public static String encrypt(String data, IvParameterSpec iv, SecretKey key) throws Exception{
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGO);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE,key,iv);
byte[] encryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(data.getBytes());
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encryptedBytes);
}
}
Explanation:
- Define AES algorithm used with CBC (Cipher Block Chaining) mode with PKCS5Padding.
- Create an instance of cipher with the given algorithm and initialize the cipher for encryption mode with the provided key and initiliazed vector.
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGO); cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE,key,iv);
- Convert the given plain text to byte array and then encrypt it.
- Converts the encrypted data into a Base64 string to make it readable and easy to store/transmit.
Decryption Using AES
To retrieve the original plain text we need to decrypt the encrypted text by using the same key and IV.
package AES;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import java.security.InvalidAlgorithmParameterException;
import java.security.InvalidKeyException;
import java.util.Base64;
public class AESDecryption {
public static final String ALGO = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
public static String decrypt(String encryptedData, IvParameterSpec iv, SecretKey key) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGO);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE,key,iv);
byte[] decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encryptedData));
return new String(decryptedBytes);
}
}
Explanation:
- Similar to AESEncryption class we create an instance of cipher for AES encryption with CBC mode and PKCS5Padding.
- This time initialze the cipher with decryption mode with same key and iv.
- Decode and decrypt the Base64 encoded and encrypted String.
- Return the decrypted String.
Running the AES Encryption and Decryption
The below code tests the encryption and decryption by using the above defined classes
package AES;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
public class AESImplementation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
SecretKey key = AESKeyProvider.generateKey();
IvParameterSpec iv = AESIVProvider.generateIv();
String PlainText = "AES Encryption and Decryption";
String encryptedText = AESEncryption.encrypt(PlainText, iv, key);
System.out.println("The encrypted Text obtained is: " + encryptedText );
String decryptedText = AESDecryption.decrypt(encryptedText,iv,key);
System.out.println("Decrypted Text obtained is: " + decryptedText );
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Output:
The encrypted Text obtained is: cdYflMA6AJTDlgZWU1W0+XqJYe7OwT1jpLobFIKlFf8= Decrypted Text obtained is: AES Encryption and Decryption
Explanation:
- Import the instances of SecretKey and IvParameterSpec by using the custom classes created above.
- Call the encrypt method of the AESEncryption to encrypt the given plain text.
- Print the obtained encrypted text.
- Retrieve the original text by using decrypt method of AESDecryption class.
- Print the decrypted message i.e original plain text.
Checkout other tutorials:
Read and Write Files in Java Using FileReader and FileWriter
Download image from URL in Java
Java program to fetch JSON data