Hello Everyone, today we are going to learn about implementing the flood fill algorithm in Java.
Here I will explain it with an example, suppose we want to color a square box with the same color, we use an algorithm called the Flood Fill algorithm.
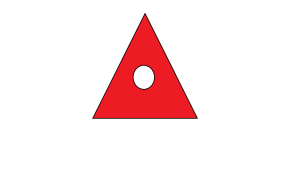
From the above picture if we see there are pixels containing in the picture it starts coloring the same color to all the pixels until it reaches the border of the other color.
We could see the triangle is colored all red until the border of the circle.
Algorithm Using Recursive Method
The recursive method means the function calls itself until it reaches the condition where it will return the result.
It will follow a few steps to solve it in the recursive method.
- Initialization: First the function will start with a particular cell (i, j)
- Checking condition: now it will check whether it satisfies the condition or not.
- Recursion: If the condition does not satisfy, then it starts calling itself.
- Return the result: once the condition is satisfied then it will return the value.
Code Using Recursive Method
public class FFA {
//recursive function
public static void FloodFillAlgo(int[][] obj, int a, int b, int targetcolor, int replacementcolor) {
if(a < 0 || a >= obj.length || b < 0 || b >= obj[0].length) {
return;
}
if (obj[a][b] != targetcolor || obj[a][b] == replacementcolor) {
return;
}
obj[a][b] = replacementcolor;
FloodFillAlgo(obj, a + 1, b, targetcolor, replacementcolor);
FloodFillAlgo(obj, a - 1, b, targetcolor, replacementcolor);
FloodFillAlgo(obj, a, b + 1, targetcolor, replacementcolor);
FloodFillAlgo(obj, a, b - 1, targetcolor, replacementcolor);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[][] obj = {
{1, 1, 2, 2, 2},
{1, 0, 2, 2, 2},
{1, 1, 2, 0, 2},
{1, 1, 0, 2, 2},
};
int targetcolor = 1;
int replacementcolor = 5;
FloodFillAlgo(obj, 1, 2, targetcolor, replacementcolor);
for(int[] row : obj) {
for(int pixel : row) {
System.out.print(pixel + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:
1 1 2 2 2 1 0 2 2 2 1 1 2 0 2 1 1 0 2 2
Algorithm Using Iterative Method
Iterative method means using loops and it will repeat the execution until the given condition is satisfied.
- Initializing; First, the loops are initialized by variables and conditions.
- Checking Condition: It will check the condition and proceed further if the condition is true else it will exit the loop.
- Execution: Executes the body of the loop.
- Update: Accordingly it will update the values of the variables.
Code Using Iterative Method
import java.util.Stack;
public class FFA {
public static void FloodFillAlgo(int[][] obj, int a, int b, int targetColor, int replacementColor) {
if (obj[a][b] != targetColor) {
return;
}
int rows = obj.length;
int cols = obj[0].length;
Stack<int[]> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(new int[]{a, b});
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int[] curr = stack.pop();
int ca = curr[0];
int cb = curr[1];
obj[ca][cb] = replacementColor;
if (ca + 1 < rows && obj[ca + 1][cb] == targetColor) {
stack.push(new int[]{ca + 1, cb});
}
if (ca - 1 >= 0 && obj[ca - 1][cb] == targetColor) {
stack.push(new int[]{ca - 1, cb});
}
if (cb + 1 < cols && obj[ca][cb + 1] == targetColor) {
stack.push(new int[]{ca, cb + 1});
}
if (ca - 1 >= 0 && obj[ca][cb - 1] == targetColor) {
stack.push(new int[]{ca, cb - 1});
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] obj = {
{1, 0, 2, 2, 2},
{1, 2, 0, 2, 2},
{1, 0, 2, 2, 2},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0}
};
int targetColor = 1;
int replacementColor = 5;
FloodFillAlgo(obj, 1, 2, targetColor, replacementColor);
for (int[] row : obj) {
for (int pixel : row) {
System.out.print(pixel + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:
1 0 2 2 2 1 2 0 2 2 1 0 2 2 2 1 1 0 0 0