Pass Argument to Tkinter button command in Python
This lesson will teach us how to pass arguments to the Tkinter button command in Python. We need to create a Tkinter button using Python and a function to pass an argument when the button is triggered, displaying the result—used argument.
how to create a pass argument to the Tkinter button using Python :
Let’s start to create a Tkinter button using Python:
import tkinter as tk
root=tk.Tk()
root.title("Button")
root.geometry("300x200")
def hello():
print("Hello codespeedy")
button=tk.Button(root,text="Click on", command=hello)
button.pack()
root.mainloop()
Output:
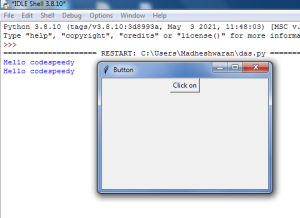
Explanation of code:
01. import tkinter as tk
- This line imports the
tkinterlibrary and assigns it the aliastk. - This allows you to use
tkinstead of the entire module name throughout the code.
02. root=tk.Tk()
- This line creates the main window for your application.
- The
tk.Tk()function is used to create a new Tkinter window. - The variable root stores this window object, which you’ll use later to manage the window’s properties and widgets.
03. root.title("Button")
- This line sets the title of the main window to “Button”. This title appears at the top of the window’s title bar.
04. root.geometry("300x200")
- This line defines the window’s geometry, Which specifies width and height.
- Here, it sets the window to be 300 pixels wide and 200 pixels high.
05. def hello():
print("Hello codespeedy")
- This line defines a function named
hello(). - The function’s body contains a single-line
print("Hello codespeedy")that prints the message “Hello code speedy” to the console when the function is called.
06. button=tk.Button(root,text="Click on", command=hello)
- This line creates a button widget. The
tk.Button()function creates a new button object and stores it in thebuttonvariable. - The first argument
(root)specifies the parent window in which the button will be displayed. - The second argument
(text=" click on")sets the text that will be displayed on the button’s face. - The most important part here is the
command=helloargument. This binds thehellofunction to the button. When the user clicks the button, thehellofunction will be executed.
07. button.pack()
- This line arranges the button widget within the main window. The
pack()method is a layout manager in Tkinter that helps you position widgets within the window. - In this case, packing the button places it in the window without any specific constraints, allowing it to fill available space.
08. root.mainloop()
- This line starts the main event loop of the Tkinter application.
- The
mainloop()method listens for user interactions and updates the GUI accordingly. This line keeps the applications running until the user closes the window, at which pointmainloop()finishes.
In this lesson, now we have successfully created a pass argument Tkinter button in Python.