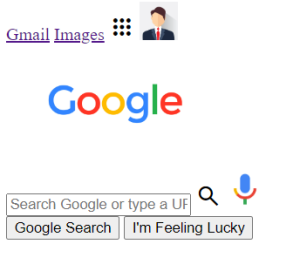
In this tutorial, you will be going through the steps of replicating the google homepage with the help of HTML and CSS. This is a very simple guide which anyone can understand and replicate the google homepage by their own. Let’s dive into the contents:
Setting up the HTML page
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Material+Symbols+Outlined"/>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<title>Google Homepage</title>
</head>
<body>
<nav>
<a href="" class="nav">Gmail</a>
<a href="" class="nav">Images</a>
<span class="material-symbols-outlined apps">apps</span>
<img src="image/avt.jpg" alt="" class="avatar">
</nav>
<div class="google">
<img src="image/google.jpg" alt="" class="gimg">
<div class="search">
<input type="text" placeholder="Search Google or type a URL">
<span class="material-symbols-outlined searchicon">search</span>
<img src="image/mike.jpg" alt="" class="mic">
</div>
<div class="sbut">
<input type="button" value="Google Search">
<input type="button" value="I'm Feeling Lucky">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Explanation
- <!DOCTYPE html>: Defines the document type and html version.
- <html lang=”en”>: Specifies language of document as english.
- <head>: Contains meta-information about the HTML document.
- <meta charset=”UTF-8″>: Specifies the character encoding to UTF-8.
- <meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0″>: Ensures the webpage is properly scaled and responsive.
- <link rel=”stylesheet” href=”https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Material+Symbols+Outlined”/>: This line includes a link to a Google Fonts Stylesheet, which includes the “Material Symbol Outlined” icon set.
- <link rel=”stylesheet” href=”style.css”>: Links an external CSS file (style.css) for styling purpose.
- <title>Google Homepage</title>: Sets the title of the web page as “Google Homepage”.
- <body>: Contains the content that will be displayed on the web page.
- <nav>: This is a navigation bar containing links and icons.
- <a href=”” class=”nav”>Gmail</a>: A linked labelled “Gmail”. The ‘href=’ attribute is empty so it doesn’t link anywhere for now.
- <a href=”” class=”nav”>Images</a>: Another link, similar to the first one but this one says ‘images’.
- <span class=”material-symbols-outlined apps”>apps</span>: This uses the material symbols icon font to display an ‘apps’ icon.
- <img src=”image/avt.jpg” alt=”” class=”avatar”>: An image representing the user’s avatar. The ‘src’ attribute points to ‘image/avt.jpg’, which is the image files location.
- <div class=”google”>: This contains the Google logo and the search functionality.
- <img src=”image/google.jpg” alt=”” class=”gimg”>: This displays an image of the Google logo.
- <div class=”search”>: This contains the search bar.
- <input type=”text” placeholder=”Search Google or type a URL”>: This is a input text field where user can type their search query or URL.
- <span class=”material-symbols-outlined searchicon”>search</span>: This displays a search hiker next to the input field using the materials symbol icon set.
- <img src=”image/mike.jpg” alt=”” class=”mic”>: This displays an image of a microphone, likely representing voice search functionality.
- <div class=”sbut”>: This section contains the search buttons.
- <input type=”button” value=”Google Search”>: A button labelled “Google Search”.
- <input type=”button” value=”I’m Feeling Lucky”>: A button labelled “I’m Feeling Lucky”.
Output:
Adding CSS Styles
body{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
background: #fff;
}
.google{
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%,-100%);
}
.gimg{
position: relative;
width: 380px;
top: 80px;
}
.search{
width: 500px;
height: 45px;
position: absolute;
transform: translate(-20%,50%);
}
.search input{
position: absolute;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
border: 1px solid #00000059;
left: 0;
border-radius: 20px;
padding: 0 40px 0 45px;
outline: none;
box-shadow: 0 2px 10px -2px;
font-size: 16px;
}
.searchicon{
position: absolute;
z-index: 1;
font-size: 21px;
top: 13px;
left: 18px;
color: #777;
}
.mic{
position: absolute;
width: 25px;
right: -65px;
top: 10px;
}
.sbut{
position: relative;
top: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
.sbut input{
background: #D5D5D5;
border: none;
padding: 8px 20px;
margin: 10px;
color: #000;
border-radius: 5px;
outline: none;
}
.sbut input:hover{
cursor: pointer;
background: #909090;
color: #000;
box-shadow: 0 0 2px;
}
nav{
float: right;
}
.avatar{
width: 35px;
border-radius: 50%;
margin: 10px 20px 0 0;
}
.nav{
color: #555;
text-decoration: none;
top: -12px;
position: relative;
margin: 5px;
}
.nav:hover{
text-decoration: underline;
}
.apps{
position: relative;
margin: 10px;
top: -6px;
color: #555;
cursor: pointer;
}
Explanation
- ‘body‘
- Sets the margin and padding to zero. The background color is set to white.
- ‘.google‘
- The Google section is centered both horizontally and vertically.
- The ‘transform: translate(-50%,-100%);’ adjustment further fine-tunes the positioning, moving it slightly upward.
- ‘.gimg‘
- Positions the Google logo relative to its container.
- Sets the logo’s width 380px and moves it 80px down.
- ‘.search‘
- Set the size of the search bar 500px wide and 45px tall.
- Positions it’s slightly offset using ‘transform: translate(-20%,-50%);’.
- ‘.search input‘
- Positions the input field within the search bar.
- Makes it full width and height, with a border and rounded corners.
- Adds padding inside and sets a box shadow for depth.
- Sets font-size to 16px.
- ‘.searchicon‘
- Positions the search icon within the search bar.
- Ensures it appears on top.
- Sets the font size to 21px and colours it grey.
- ‘.mic‘
- Positions the microphone icon inside the search bar.
- Sets its width to 25px and places it to the right inside the search bar.
- ‘.sbut‘
- Positions the container for the buttons 100px below the search bar.
- Centres the button.
- ‘.sbut input‘
- Styles the button with grey background, rounded corners and padding.
- Removes borders and outlines for a clean look.
- Add spacing between the buttons using ‘margin’.
- ”.sbut input:hover”
- Changes the background to darker grey and adds subtle shadow when hovering.
- Ensure the cursor changes to a pointer to indicate it’s clickable.
- ‘nav‘
- Float the navigation items to the right of the page.
- ‘.avatar‘
- Stage the users avatar with a width of 35px and rounded corners to make it circular.
- Add some margin for spacing.
- ‘.nav‘
- Style the navigation links with a grey colour and remove the underline.
- Positions them above their original position and adds margin for spacing.
- ‘.nav:hover‘
- Underlines the navigation links when hovered.
- ‘.apps‘
- Positions the “apps” icon.
- Colours it grey and changes cursor to pointer when hovered.
Output
Conclusion
The HTML and CSS code works together to build a clean and functional Google-like homepage replica. The HTML provides the structure with navigation, logo, search bar and button while the CSS ensures these elements are well-styled and positioned for a user-friendly, Google-inspired design.
Have a Happy and a Great coding!