Introduction
So, basically, Flask is a web development framework which is written in Python, and it is widely used as a web framework for creating APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) or it is a micro web framework that allows developers to build web applications quickly and easily.
Python-Flask Request
In Python-Flask the request module is an object that allows you to access the data sent from the user to the server (Client-Server), and that data is passed into your Flask Application.
There are two methods in order to get the data/ request the data:
- GET Method
- Post Method
Prerequisites
pip install Flask
pip install requests
-
from flask import Flask, request, render_template, redirect, url_for import os app = Flask(__name__) # Configure upload folder and allowed file types UPLOAD_FOLDER = 'uploads' ALLOWED_EXTENSIONS = {'png', 'jpg', 'jpeg', 'gif', 'pdf'} app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'] = UPLOAD_FOLDER # Ensure the upload folder exists os.makedirs(UPLOAD_FOLDER, exist_ok=True) def allowed_file(filename): return '.' in filename and filename.rsplit('.', 1)[1].lower() in ALLOWED_EXTENSIONS @app.route('/', methods=['GET', 'POST']) def upload_file(): if request.method == 'POST': # Check if the POST request has a file if 'file' not in request.files: return "No file part in the request" file = request.files['file'] # If no file is selected if file.filename == '': return "No file selected for uploading" if file and allowed_file(file.filename): filename = file.filename file.save(os.path.join(app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'], filename)) return f"File '{filename}' successfully uploaded!" else: return "File type not allowed" return render_template('index.html') if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug=True)Explanation
Flask(__name__): Used to create an instance of the Flask application. It sets up your Flask app and acts as the central object for the application, managing routing, configuration, and other functionalities.
- @app.route: Decorator in Flask used to define the URL route (or endpoint).
- UPLOAD_FOLDER: Defines where the uploaded files will be stored.
- allowed_file(): Ensures only files with specific extensions are accepted.
HTML (index.html)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>File Upload</title> </head> <body> <h1>Upload File</h1> <form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="file" name="file"> <button type="submit">Upload</button> </form> </body> </html>
Write the above code in the index.html which should be created in the templates folder
Output:
You can access the webpage using the endpoint http://127.0.0.1:5000 and see the JSON file which will look as
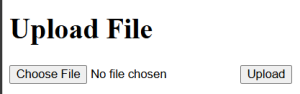
You can upload the file and check the file in the uploads file in your compiler.
Conclusion
Now there are better solutions that work faster and are more reliable. There are JavaScript libraries like jQuery that have form plugins to ease the construction of progress bar.
Because the common pattern for file uploads exists almost unchanged in all applications dealing with uploads, there are also some Flask extensions that implement a full-fledged upload mechanism that allows controlling which file extensions are allowed to be uploaded.