Cookies are small pieces of information stored on the user’s computer by their web browser. They are widely used for storing user preferences, session information, and activity tracking. In this blog, we’ll explore how to work with cookies in JavaScript using simple and understandable code examples.
What are cookies?
Cookies store user-specific information like preferences, login sessions, and other data that needs to persist across different pages or visits. Each cookie is a name-value pair and can have an expiration date, a path, and other attributes.
Understanding cookies:
Cookies have key-value pairs, and additionally, they have several attributes for example, they include expiration time, path, and domain. Here’s a basic breakdown of the essential attributes of a cookie:
- Name: The name of the cookie.
- Value: The value associated with the cookie name.
- Expires: The expiration date of the cookie.
- Path: The path where the cookie is accessible.
- Domain: The domain where the cookie is accessible.
Basic Operations of Cookies:
- Setting a cookie.
- Getting a cookie.
- Deleting a cookie.
Example of cookies in JavaScript
Let’s look at an example of how to set (create), get (read), and delete cookies. Here, the cookie stores the information of a user.
<!--for example this is a cookie.html file--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body> <input type="button" value="Set Cookie" onclick="setCookie()"> <br> <br> <input type="button" value="Get Cookie" onclick="getCookie()"> <br> <br> <input type="button" value="Delete Cookie" onclick="deleteCookie()"> <br> <br> <input type="button" value="Display cookies" onclick="displayCookie()"> <script src=cookie.js> </script> </body> </html>
The HTML code creates a simple webpage with buttons to set, get, delete, and display cookies. Each button triggers a respective JavaScript function (setCookie(), getCookie(), deleteCookie(), displayCookie()) defined in an external script file named cookie.js. This enables interaction with browser cookies through the user interface.
output of HTML code:
<!--This is a cookie.js file-->
<!-- setting, getting, deleting, and displaying cookies-->
function setCookie()
{
document.cookie="name=user_name";
cookie = document.cookie;
}
function getCookie()
{
if(cookie.length!=0)
{
alert(cookie);
}
else
{
alert("Cookie not available");
}
}
function deleteCookie()
{
document.cookie=cookie+";max-age=0";
cookie=document.cookie;
alert("Cookie is deleted");
}
function displayCookie()
{
if(cookie!=0)
{
alert(cookie);
}
else{
alert("Cookie not available");
}
}
The JavaScript code defines functions to manage cookies: setCookie() creates a cookie with name=user_name; getCookie() alerts the cookie if it exists; deleteCookie() deletes the cookie by setting its max-age to 0 and alerts the user; displayCookie() alerts the cookie if it exists. These functions interact with the document.cookie property.
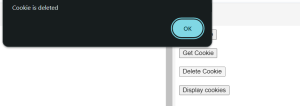
output of JavaScript Code:
After setting the cookie we have to get the cookie, below output shows the get operation of the cookie.The below output shows the operation of the Deleting cookie.
Conclusion:
By using these simple JavaScript functions, you can easily manage cookies in your web applications. Setting, getting, and deleting cookies are fundamental operations that allow you to store and retrieve user data effectively. This example demonstrates a basic yet practical approach to handling cookies, providing a foundation for more complex implementations.