File Zipper via Huffman Coding in Java
By Apoorwa
File zipper via Huffman coding is a data compression technique used to reduce the size of a file by encoding its contents using Huffman coding in java.
Huffman coding is a lossless data compression algorithm. In this algorithm, a variable-length code is assigned to input different characters. The code length is related to how frequently characters are used. Most frequent characters have the smallest codes and longer codes for the least frequent characters.
The process involves two main parts:
1. Constructing a Huffman tree depending on the frequency of characters through minimum priority queue(The natural ordering of Priority Queue has the least or smallest element at the head of the queue and thus the ordering is ascending) and basic tree implementation.
3. The Huffman tree is constructed by adding two least frequencies of the leaf nodes(characters) and forming the parent node. The process is continued until one single node is achieved which will be the root node.
2. Generating Huffman codes by traversing through the root to each leaf node for every character. The left branch corresponds to appending a '0' to the code, and the right branch corresponds to appending a '1'.
3. The file will be compressed by replacing every single character with its corresponding Huffman code.
Hence, reducing the size of the original data. This results in a more compact representation of the original data, allowing for efficient storage and transmission.
Example for constructing a Huffman tree:
Huffman tree generated from the exact frequencies of the text "this is an example of a Huffman tree". The Huffman tree constructed from the character and its frequencies will be as follows: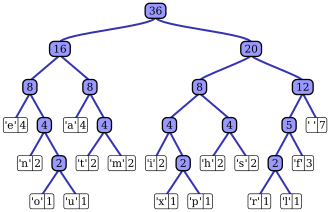
The frequencies and Huffman codes of each character are:
| Char | Freq | Code |
|---|---|---|
| space | 7 | 111 |
| a | 4 | 010 |
| e | 4 | 000 |
| f | 3 | 1101 |
| h | 2 | 1010 |
| i | 2 | 1000 |
| m | 2 | 0111 |
| n | 2 | 0010 |
| s | 2 | 1011 |
| t | 2 | 0110 |
| l | 1 | 11001 |
| o | 1 | 00110 |
| p | 1 | 10011 |
| r | 1 | 11000 |
| u | 1 | 00111 |
| x | 1 | 10010 |
Hence, for a character represented by 8 bits can be represented in 3,4 or 5 bits reducing the overall size of the file and implementing lossless data copression.The below code is written in java which by using Priority Queue and Hashmaps for Huffman Coding Algorithm and modules like Swing and Awt for creating a simple Graphics User Interface by using JLabels and JButtons for displaying the input file and and output file sizes:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class HuffmanNode implements Comparable {
char data;
int frequency;
HuffmanNode left, right;
public HuffmanNode(char data, int frequency) { // defining the node of a tree
this.data = data;
this.frequency = frequency;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(HuffmanNode node) {
return this.frequency - node.frequency;
}
}
public class HuffmanCompression {
private static HashMap<Character, String> huffmanCodes = new HashMap<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
new HuffmanCompressionGUI();
}
});
}
private static HuffmanNode buildHuffmanTree(HashMap<Character, Integer> charFrequency) {
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(); //for storing frequency in ascending order
for (char c : charFrequency.keySet()) {
priorityQueue.add(new HuffmanNode(c, charFrequency.get(c)));
}
while (priorityQueue.size() > 1) { //constructing the Huffman Tree
HuffmanNode left = priorityQueue.poll();
HuffmanNode right = priorityQueue.poll();
HuffmanNode mergedNode = new HuffmanNode('\0', left.frequency + right.frequency);
mergedNode.left = left;
mergedNode.right = right;
priorityQueue.add(mergedNode);
}
return priorityQueue.poll();
}
private static void generateHuffmanCodes(HuffmanNode root, String code) {
if (root == null) {
return;
} //generating Huffman Codes
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
huffmanCodes.put(root.data, code);
}
generateHuffmanCodes(root.left, code + "0");
generateHuffmanCodes(root.right, code + "1");
}
private static String compressText(String inputText) {
StringBuilder compressedText = new StringBuilder();
for (char c : inputText.toCharArray()) {
compressedText.append(huffmanCodes.get(c));
}
return compressedText.toString();
}
private static String convertToBinaryString(String compressedText) {
StringBuilder binaryString = new StringBuilder();
int len = compressedText.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i += 8) {
String byteStr = compressedText.substring(i, Math.min(i + 8, len));
int byteValue = Integer.parseInt(byteStr, 2);
binaryString.append((char) byteValue);
}
return binaryString.toString();
}
static void compressFile(File inputFile, File outputFile) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(inputFile));
StringBuilder inputText = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) { //reading the input file
inputText.append(line).append("\n");
}
reader.close();
HashMap<Character, Integer> charFrequency = new HashMap<>();
for (char c : inputText.toString().toCharArray()) {
charFrequency.put(c, charFrequency.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
HuffmanNode root = buildHuffmanTree(charFrequency);
generateHuffmanCodes(root, "");
String compressedText = compressText(inputText.toString());
String binaryString = convertToBinaryString(compressedText);
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(outputFile));
writer.write(binaryString);
writer.close();
}
}
class HuffmanCompressionGUI extends JFrame {
private JLabel originalSizeLabel, reducedSizeLabel;
private JButton compressButton;
private JFileChooser fileChooser;
public HuffmanCompressionGUI() {
super("Huffman Compression");
originalSizeLabel = new JLabel("Original Size: N/A");
reducedSizeLabel = new JLabel("Reduced Size: N/A");
compressButton = new JButton("Compress");
fileChooser = new JFileChooser();
compressButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int returnValue = fileChooser.showOpenDialog(HuffmanCompressionGUI.this);
if (returnValue == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) {
File inputFile = fileChooser.getSelectedFile();
File outputFile = new File(inputFile.getParent(), "compressed.txt");
try {
HuffmanCompression.compressFile(inputFile, outputFile);
long originalSize = inputFile.length();
long reducedSize = outputFile.length();
originalSizeLabel.setText("Original Size: " + originalSize + " bytes");
reducedSizeLabel.setText("Reduced Size: " + reducedSize + " bytes");
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(HuffmanCompressionGUI.this,
"Compression completed successfully.\nCompressed file saved as 'compressed.txt'.",
"Success", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
} catch (IOException ex) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(HuffmanCompressionGUI.this,
"Error occurred while compressing the file.",
"Error", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
add(compressButton);
add(originalSizeLabel);
add(reducedSizeLabel);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
pack();
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setVisible(true);
}
}
The initial window displayed after running the code will be:
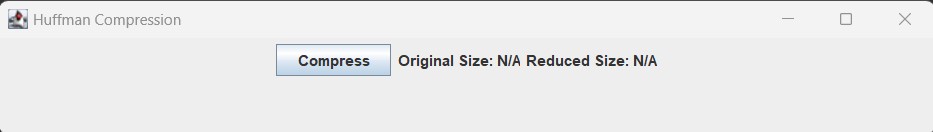
Select the file:
The compressed file will be saved as:
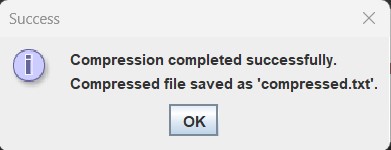
The final output displaying the original as well as the compressed size:
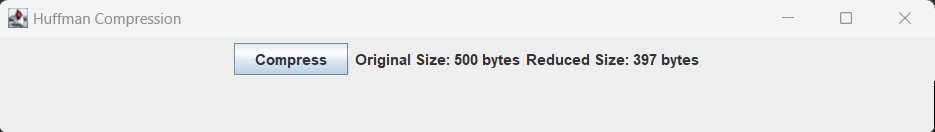
File zipper via Huffman coding is suitable for text-based data or data with repetitive patterns, where Huffman coding can effectively reduce the file size. However, for highly compressed or already compressed data (e.g., JPEG images), Huffman coding may not provide significant compression gains.
The process of Huffman coding is relatively simple, yet it can yield substantial compression results. It is widely used in various applications where efficient data storage and transmission are required.
Submitted by Apoorwa (Apoorwa)
Download packets of source code on Coders Packet
Comments