Personal Library Manager using Python
By Sahil Raj
This project involves writing a Python code to manage a library of books. This is to give an idea of how a library with a large number of books keeps track of all the books.
INTRODUCTION
This project contains a file named app.py that contains a database of books containing information like Author, Title, and reads. This is the basic implementation of library management. It provides a glance at the management technique that a library might use to keep track of all the books. This information keeps getting updated from time to time as more books come into the library and if any other information needs to be updated.
All the data is stored in the `library.db` file which is present in the folder. Here we use Python programming to create the project.
Note: There is a lot of scope for improvement in this project. One can add information like the book shelve number representing where it is kept and book counts present, total book counts. To make it more realistic, a table can be created for users who took which book and many more.
HOW TO RUN THE CODE
1. Extract the zipped file given below.
2. Open the extracted folder.
3. Open the file named "app.py" in your preferred IDE.
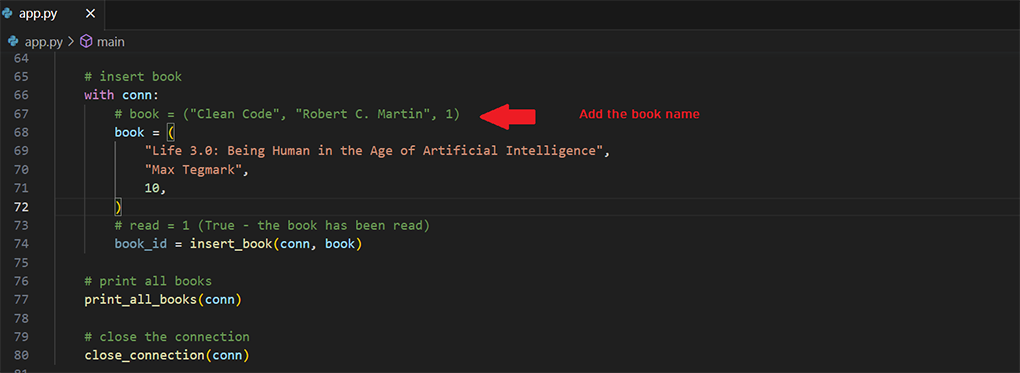
4. Modify the book name that is to be inserted in the 'books' database.
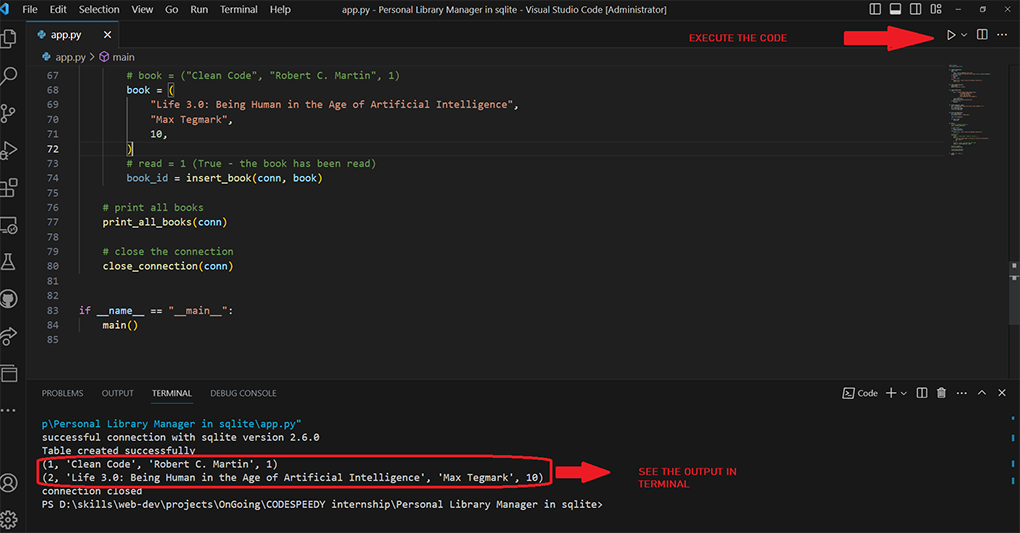
5. Execute the Python file in the terminal.
6. See the output.
DEMO EXECUTION
CODE EXPLANATION
1. We are using `sqlite3` package. SQLite is a database engine.
2. `connect_to_db` function: We're trying to connect to a database file called "library.db". If the connection is successful, we will see a print message saying "successful connection with sqlite version ...".Finally, if everything works correctly, we return the connection. If it fails, we print an error message.
3. `disconnect_from_db` function: To close the database connection.
4. `set_up_table` function: Here, we're setting up the 'books' table in the database if it doesn't already exist. The table has four fields - id, title, author, and read. If the table creation is successful, we print a success message, otherwise, we print the error message.
5. `add_new_book` function: This function takes a book (which is a tuple of three values: title, author, and read) and inserts it into the books table in the database.
6. `display_all_books` function: It prints all the rows from the 'books' table in the database on our console.
7. `main` function: Here's where the action happens. We start by creating a connection to the database. Then, we create our 'books' table (if it doesn't already exist). Next, we insert a book into the 'books' table. After that, we print out all the books that are present in the 'books' table. Finally, we close the connection to the database.
8. The last two lines of the script are used to convey if we run this script directly (as opposed to importing it as a module), we should call the main function.
Submitted by Sahil Raj (rajsahilcoder)
Download packets of source code on Coders Packet
Comments